오늘은 Values, Names, Functions and Evaluations에 대해서 포스팅 할 것이다.
▶ Types and Values
- Type is a set of values
- Int : {-2147483648, ..., -1, 0, 1, ..., 2147483647} // 32-bit integers
- Double : 64-bit floating point numbers
- Boolean : {true, false}
- ...
여기서 Java랑 비슷하게 Int 타입 범위에는 제한이 있다는 걸 기억해 두는 것이 좋다. 대충 2 x 10^9 로 암기해두자.
▶ Expression
교수님이 한 수업 당 최소 50번 언급하시는 그 단어,,, 익스프레션,,,,
Expression은 values, names, primitive operation으로 구성된 계산할(?) 덩어리라고 생각하면 좋다
예를 들면 1+2 는 expression
def a = 1 + (2+3)
def b = 3 + a*4
▶ Evaluations
이것도 익스프레션 뺨치게 교수님께서 자주 언급하시는 단어다
Evaluations 의 정확한 정의는 Reducing an expression into a Value
쉽게 말하면 expression을 value로 계산하는 규칙 정도로 생각하면 된다. value가 아니면 계속 evaluate 하면 됨.
Strategy
- Take a name or an operator (outer to inner)
- (name) Replace the name with its associated expression
- (name) Evalute the expression
- (operator) Evalute its operands (left -> right)
- (operator) Apply the operator to its operands
위에서 정의했던 코드를 참고하자
def a = 1 + (2+3)
def b = 3 + a*4여기에서 5+b 라는 연산을 수행하면
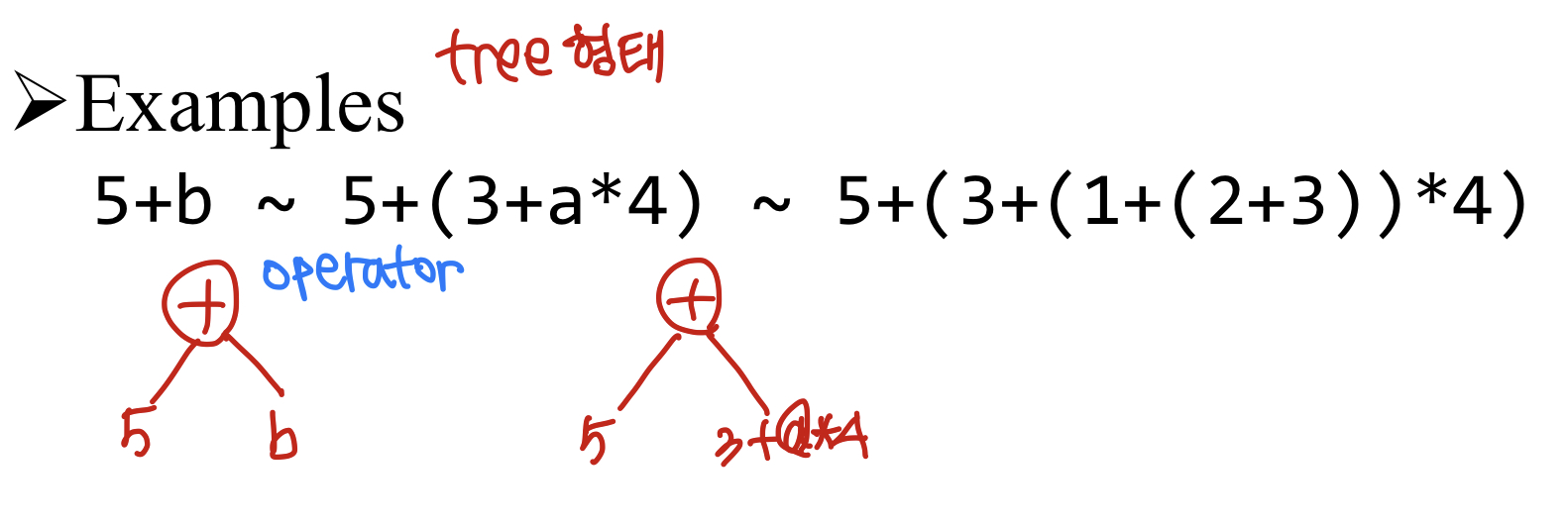
5+b ~ 5+(3+a*4) ~ 5+(3+(1+(2+3))*4) ~ ... ~ 32
이러한 순서로 작동된다.
트리 형태를 연상하면 이해하기 좋다.
▶ Functions
function은 parameters 를 가지고 있는 expression 을 의미한다. (인자가 있는 expression)
def f(x:Int):Int = x+a여기에서 함수 f는 parameter x를 가지고 있다.
x:Int 는 인자 x가 정수타입이라는 것을 알려주는 것이고, f():Int 는 함수값이 정수타입이라는 것을 알려준다.
▶ Evaluation by substitution
- (function) Evaluate its operands
- (function) Replace the function apllication by the expression of the function
- Replace its parameters with operands
Q. operand와 parameter의 차이
parameter은 x 같이 정의할 때 매개변수로 사용하는 애를 말하고, operand는 f(3)이면 여기서 3이 operand이다.
function evaluation을 이해할 수 있는 예시이다.
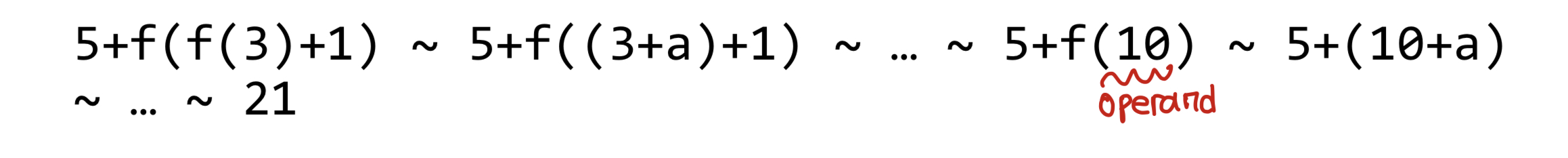
▶ Recursion
- recursion은 X의 정의에 X가 사용되는 것이다.
- 반복을 하는 강력한 메커니즘이다.
- 복잡하지 않고 단순 rewriting에 불과함.
예시 코드를 보자.
def sum(n:Int):Int =
if (n<=0)
0
else
n + sum(n-1)1부터 n까지의 자연수를 더하는 함수를 재귀를 이용해 정의한 것이다.
(아 그리고 스칼라는 파이썬이랑 다르게 indentation에 민감하지 않다. 다만 가독성을 위해서 indentation은 지키는걸로)
위의 코드는 아래와 같은 순서로 연산된다.

▶ Termination / Divergence
termination은 value를 reduce 해내는 것.
divergence는 영원히 reduce 하는 것. (무한루프)
divergence의 간단한 예시를 보자
def loop:Int = loop
def a = 1 + 2 + aloop를 정의했는데 인자가 없어서 무한루프에 빠지게 된다.
아래 a를 정의한 곳에서도 무한루프에 빠진다.
여기까지가 2차시 수업 내용이다 끗 *~*v
'학교 공부 > 프로그래밍원리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PART 2 - Object-Oriented Programming (1) (0) | 2022.10.23 |
|---|---|
| PART 1 - Exception & Handling , DataType (0929) (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| HW2 - Exercise 2 (0) | 2022.10.19 |
| PART 1 - Higher Order Functions (0922) (0) | 2022.10.18 |
| PART 1 - Functional Programming with Function Applications (2) (0) | 2022.09.29 |


